How Cybersecurity Helps Manage Risks in an Enterprise (Part 1)
Enterprise risk encompasses all potential events that could negatively impact an organisation’s ability to achieve its objectives. These risks can arise from various sources, including operational failures, regulatory compliance issues, financial uncertainties, and cybersecurity threats. As cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, organisations must prioritise cybersecurity as a fundamental component of their risk management framework. In today’s digital landscape, organisations face an array of risks that can threaten their operations, reputation, and financial stability. Moreover, as cyber threats become increasingly sophisticated, organisations must prioritise cybersecurity as a fundamental component of their risk management framework.
I typically like to say that cybersecurity, as popular as it has become, would not exist without these risks, as it is the identification of these risks that now gives rise to the need for security in cyberspace, especially risks that can either be eliminated, minimised, or mitigated. That said, we can say that cybersecurity is much more than a technical requirement, but more of a significant part of enterprise risk management.
This article seeks to look at how we can leverage technology to mitigate or combat risks in an organisation or enterprise.
Ponder this for a second: Is cybersecurity crucial? The resounding answer is ‘yes’. It shields your organisation’s precious information assets, which are under constant menace from various dangers: ransomware, data leaks, and malware—all compromising asset value. And the primary aim is to curtail financial fallout as far as possible. Efficient practices in cybersecurity also make certain that data remains available and its integrity intact, thus lowering business operation risks.
The Role of Cybersecurity in Risk Management
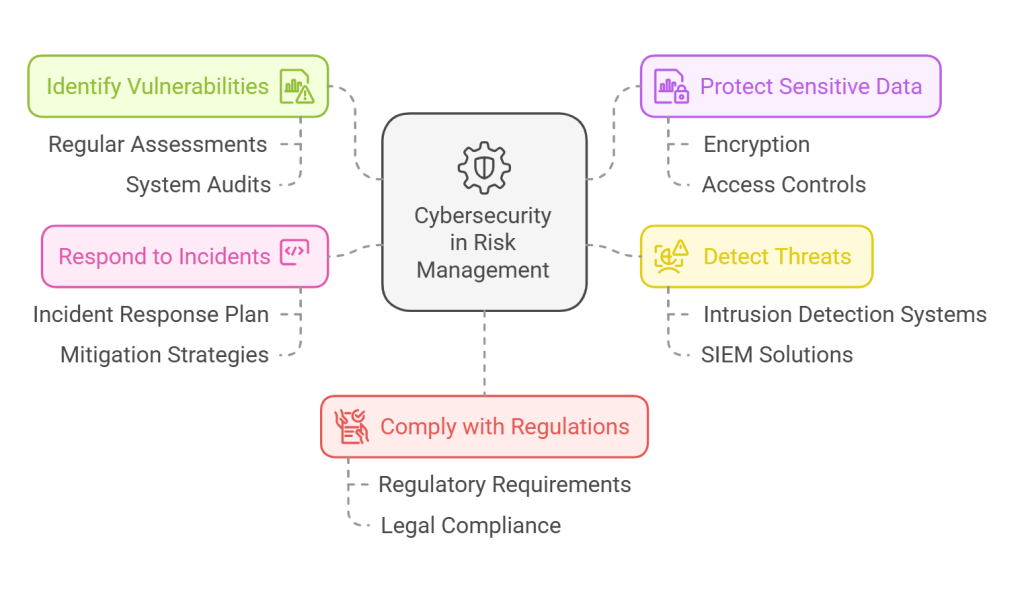
Cybersecurity serves as a foundational element in an enterprise’s risk management strategy. By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, organisations can:
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Regular assessments and audits help identify weaknesses in systems and processes that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
- Protect Sensitive Data: Encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention technologies safeguard sensitive information from unauthorised access and breaches.
- Detect Threats: Advanced threat detection tools, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, enable organisations to monitor their networks for suspicious activities in real-time.
- Respond to Incidents: An effective incident response plan, supported by cybersecurity technologies, ensures that organisations can quickly address and mitigate the impact of security breaches.
- Comply with Regulations: Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements regarding data protection. Cybersecurity technologies help organisations comply with these regulations, reducing the risk of legal penalties and reputational damage.
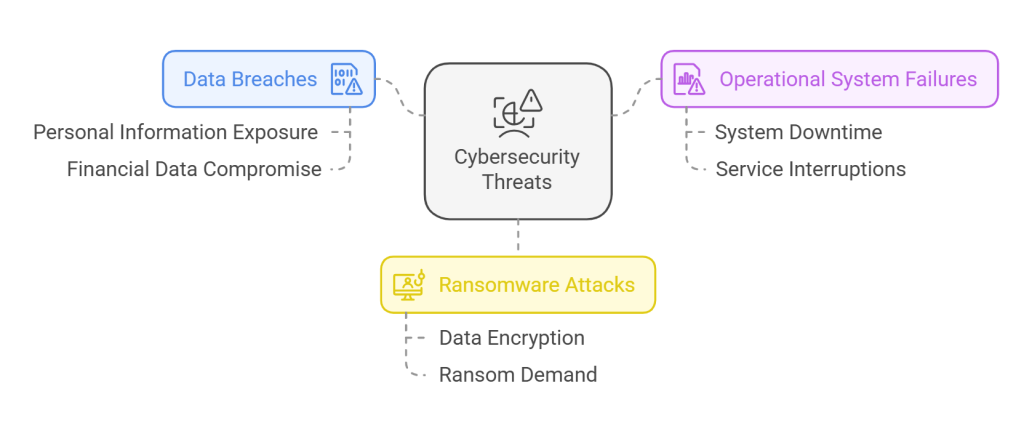
Very quickly, we would classify the outcomes of unbridled risks into just 3 simple categories to make them easy to understand. However, the common parlance for describing the impact of these attacks is to use the word “hack” or to simply state, “We have been hacked!!!”
- Data breaches
Data breaches relate to unauthorised intrusions, stealing, or exposure of confidential information. This can span from personal details, financial specifics, and classified trade information, to vital intellectual assets. The backlash of data breaches can be hefty as it potentially leads to considerable monetary losses through penalties and client reimbursements, eroding customer trust along with detrimental reputation impact and legal ramifications. The eminent risk correlated with data breaches is heightened by the rising digitalisation in operations and swelling volumes of data repositories maintained by entities.
2. Operational system failures
Operational system failures include disturbances within an organisation’s IT foundation leading to blocked access to pivotal systems and information repositories. This could stem from cyber onslaughts, hardware or software malfunctions, or even mishaps caused by human error. Effects could oscillate from operational lags and productivity decline up to full-scale business outages, which could lead to sizeable financial losses coupled with detrimental impacts on reputation.
In this category, we have denial of service attacks amongst other attacks that would cause service degradation or complete outages.
3. Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware assaults are unique brands of cyberattacks wherein malicious codes lock an organisation’s valuable data, making it inaccessible until a bounty is remunerated. Ransomware attackers often insist on payments through cryptocurrency in exchange for unlocking tools.
Factors like deficient security provisions, absence of encryption, and weak access protocols can cause an organisation to become an easy target for cyber felons to instigate breaches or perform ransomware attacks.
For identifying, gauging, and managing these risks while assuring business steadiness and toughness, a concrete risk management strategy is required, which of course includes a solid cybersecurity plan. Understanding these risks allows companies to introduce laser-focused strategies for protecting their digital valuables and apply diverse controls to reduce the likelihood of negative instances.
These strategies, however, are not all about technology; there is a need for policies, standards, and procedures that contribute towards risk reduction. In simpler terms, cybersecurity forms an integral slice of an enterprise’s risk management strategy—safeguarding assets and ensuring continuity and longevity of business.
In the subsequent parts of this article, we shall consider the impact and repercussions of not having the necessary technology risk management and, by extension, cybersecurity strategy in place.
=====================================
This article was also published on LinkedIn.
You can read Part 2 of this article here.



